Terms & Concepts
It’s time to understand all the terms and concepts we’ve used so far an more. So, let’s get started!
Consumer: A consumer is a private individual, not an organization or a business.
SMB: Small and Medium Business (SMBs) are local business such as restaurants, hotels, with a limited amount of employees. While startups are similar to SMBs in amount of employees they are very different than them in terms of revenue and business models and are therefore categorized separately from SMBs.
Startup: A Startup is a human institution, a company, or a team designed to create a new product or service under conditions of extreme uncertainty such as an unknown market, uneducated market, first product of it’s kind and more..
MLE: Medium and Large Enterprises refers to companies with 100+ employees (medium) or with 500+ employee (large). Examples of enterprises would be Adobe, Microsoft, Salesforce, Intel and more.
Consumer Facing: Consumer facing products and services target private individuals. Facebook, SnapChat, Tinder, Spotify are all consumer facing products
Business Facing: Business facing products and services target SMBs, Startups or MLEs. SalesForce, LinkedIn Recruiter, Slack, Facebook Workplace are all business facing products
Enterprise Facing: The reason Enterprise is separated from business facing, is due to the fact that the sales process is a lot longer filled with much more friction for enterprise companies when in startups or SMBs in barely exists. Creating Enterprise facing products entails the understanding the getting the first customer will take a while, Vs. a consumer facing product which can possibly go viral in days.
CEO: The Chief Executive Officer is the leader of the entire company, he carries his attention wherever it’s needed most as well as oversee the entire company.
CMO: The Chief Marketing Officer manages the entire marketing efforts and employees that manage them.
CTO: The Chief Technology Officer managers the entire developer team, project managers, and IT department.
COO: The Chief Operations Manager oversees the entire company and is responsible for the entire operations of the company, including office management, supplier management, resource management(cars, flights, etc), making sure each all departments have the personnel they need and more.
CFO: The Chief Financial Officer oversees the company spending, burn, revenue, taxes, and more.
Burn rate: The burn rate is a measure of how long a company can keep operating until it has to seek more financing. Burn rate is normally used to describe the rate at which a new company is spending its venture capital to finance overhead before generating positive cash flow from operations; it is a measure of negative cash flow. Burn rate is usually quoted in terms of cash spent per month.
Onboarding: Refers to a grace period of learning, and depends highly on context. When speaking of employee it refers to the time it takes for the employee to learn the ropes and start being productive. When speaking of user onboarding refers to a tutorial or teaching session at the beginning of using the product.
Lead / Prospect: a lead is an individual or organization with an interest in what you are selling. The interest is expressed by sharing contact information, like an email, a phone number, or even a social media handle.
Cold Lead - Is a lead which either hasn’t heard of our brand and product or one which just doesn’t have us on his mind. Just because a lead is cold, doesn’t mean that they can’t be nurtured into becoming a paying customer.
Hot Lead - It is a lead who recently showed interest in our product in one way or another, like leaving his details on our website, for instance.
Customer: A customer is a person or company who had purchased our product.
Audience Cohort: Audiences can be segmented or divided to different groups called Cohorts according to models such as the customer lifecycle or by month of registration. Splitting up all our leads into cohorts an looking at their behavior & revenue grants a lot of insight. Here are two examples of how of segmented cohorts of the target audience:
By behavior and converison rate:

By month of registration
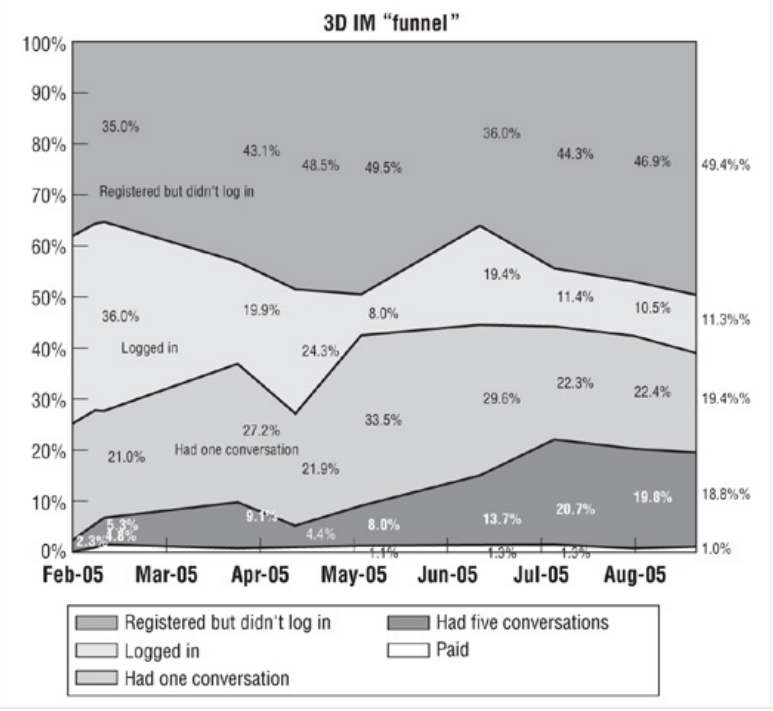
Friction: Refers to an evidence that something is causing delay or failure, depends highly on context, when speaking of user friction indicates that users don’t convert at some point. when speaking of project it indicates that someone or some group of people are causing delay and noise. A lot of friction at one point causes a bottleneck.
MRD: The Market Requirements Document gives out the layout for the competitors of our product, as well as our target audience, their demographics, personas, concerns and more.
USP: The Unique Selling Points sometimes referred to as Unique Selling Proposition is a clear statement that describes the unique benefit of our product, how it solves a customer’s needs and what distinguishes use from the competition.
Persona: A persona is a model of a person or organization which we work with in one way or another, its generally based on user research and incorporates the needs, goals, demographics, concerns and observed behavior patterns of our target audience.
A User Personas describe how different types of users may want to use our product and how they may learn of it and how to use it. They aren’t necessarily the ones who bought the product.
A Buyer Persona describe hot different types of leads may want to view our product before buying and a how the learn of the product and what considerations drive them to buy
Buyer and user personas often have different goals and expectations. The main differences are: Buyers aren’t necessarily users - Take for instance child’s toy in which the parent buys it but the child uses it. User personas focus much more and on the details and ease of use, Buyer personas are more interested in higher level goals such as feature set.
Customer Acquisition: The act of attracting qualified leads and converting them into paying customers, The cost associated with the customer acquisition process is an important measure for a business to evaluate in combination with how much value having each customer typically brings to the business.
Customer Engagement: The act of engaging the target audience to stay and use our website or product continuously, with long session durations, and many sessions per day/week/month. This can be done within the product or it’s content, on social media or on our organic website and for different audience cohorts such as visitors, prospects, or active customers.
Customer Retention: The act of retaining the customer throughout billable periods of the year, depending on the pricing it could mean keeping the month for month, or by usage. This is extremely important, if you acquire a lot of customers but have a low retention rate, things will go south fast.
Churn Rate: The churn rate is the weekly/monthly/yearly percentage of customers who cancel and discontinue their subscriptions. For a company to expand its clientele, its growth rate, as measured by the number of new customers, must exceed its churn rate. This rate is generally expressed as a percentage.
CAC: Customer acquisition cost (CAC) is a metric than includes all the marketing costs to Aquire one customer on average (including ads, content, landing pages and more. does not include paychecks and other operational expenses)
ARR: The Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is an average of all revenue acquired in a year and is based on the customer lifetime and amount of purchases in a year.
MRR: The Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is an average of all revenue acquired for a month for a subscription based product, yearly payments are split into 1⁄12 for each month instead of counting for the month the transaction was done.
LTV: In marketing, the Lifetime Value (LTV) is a prediction of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer. and is calculated buy averaging
$ \frac{MRR}{Number of Customers \times Churn} $
ROI: Return-on-Investment (ROI) is a metric that puts into account the the budget put into a task and the return and benefits of that task as a monetary value. It depends highly on the context and scope of the conversation - whether we’re speaking of a campaign, one of several brands, or our entire operation. When speaking of our whole operation for instance.
$ ROI = \frac{CAC}{LTV} $
Keeping tabs on the ROI of your campaigns helps you make smarter decisions about how you should be allocating resources.
MAU & DAU - The Monthly and Daily Active Users is the number of users who use your product on a regular basis. These have nothing to do with revenue but their a great indicator of customer retention and churn rate.
Demographics: User demographics are broad strokes of information about them such as nationality, residence, location, gender, race, etc.
Use Case: A use case an example or demonstration that shows the interaction between the end user and a product or service. Although use cases are most commonly used in technology settings, these demonstrations can help effectively convey benefits to customers in marketing and sales content.
Scope: The scope of a project is the definition of what it includes what is excluded from the project.
OOS: Out of Scope refers to details which are out of scope for the project.
TBD: To be Determined (TBD), signifies something is undecided as of yet.
POC: a Proof-of-Concept (POC), in marketing, refers to a valid measurement that shows there is interest in the solution we are offering. this can be attained in various manners, such as cold calling, setting up a marketing funnel, setting up a physical booth, and more depending on the product and the target audience,
Cold Calling - Cold calling is generally referring to an outgoing phone call with a cold lead who is either unengaged with our brand or, in many cases, is hearing of it for the very first time.
Case Study: A case study is a piece of content such as an article or white-paper that presents a real world success story of someone using and benefiting from our product.
Stakeholder: Is a person, people or organization who has an interest and stake in what we’re doing such as our product or our marketing campaigns. Stakeholders are kept informed as far as the process of work continues and can affect and are affected by the strategy and execution.
Milestone: A milestone is a predefined part of project execution, for instance if you break the creation of a new campaign into 4 parts
Creation
Distribution
Result Analysis
Validation (Success/Failure)
Then each of these points would be a different milestone for creating new campaigns.
Inbound Marketing: A permission-based marketing approach that focuses on attracting leads through useful content, engagement and optimization. Coined by HubSpot CEO Brian Halligan, inbound marketing is all about developing awesome content to attract and convert qualified leads.
Outbound Marketing: Outbound marketing is a traditional method of marketing seeking to obstruct potential customer’s time by diverting their attention with ads, cold calls, and more.
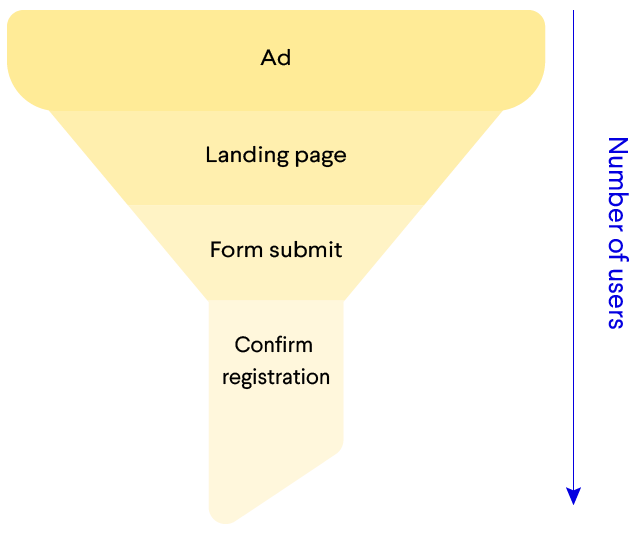
Marketing Funnel: A set of components such as posts, landing pages, articles, ads and more that are used in a set order aiming for customer acquisition. For Instance:
Copy: Copywriting is the act of writing text for the marketing purposes. The product, called copy, is written content that aims to increase brand awareness and ultimately persuade a person or group to take a particular action.
Design: Design in marketing is more than the logos, images, page layouts, and unique fonts that comprise your brand’s aesthetic; it is the central entity that connects your company to your brand, and ultimately to your customer.
Landing Page: A campaign-specific page distinct from your main website that has one goal and one call to action. A landing page could be a lead generation page or a click-through page for eCommerce. You should always send campaign traffic to a dedicated landing page.
CTA: The Call to Action is the one thing you want people to click on your page. Your call to action is the big shiny button you’re trying to steer attention toward, the “ask” every campaign is built around, your landing page’s raison d’etre.
Optimization: The process of making something as effective and cost-efficient as possible. In conversion marketing, optimization is all about using A/B testing to achieve the highest possible return on your marketing activities with the least amount of money.
A/B Testing: A marketing experiment where two variations of a landing page, ad, email or other piece of online content are pitted against each other to determine which produces the highest conversion rate. A/B testing is the key to optimizing your marketing campaign.
Market Vertical: A Market Vertical is a specific niche within an industry. For instance, while Microsoft Dynamic CRM, SalesForce and HubSpot are CRM’s that aim to fit anyone, anywhere and are there for Horizontal products, Shedul which targets Spa’s & hair salons, Weeloy which targets restaurants, or CoWorkify are all vertical products, targeting a specific market vertical instead of the whole market.
KPI / OKR: A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a metric that indicates of success or failure of a product, page, campaign, ad, etc. This metric has been specifically defined by the team as a KPI, instead of just another metric. An Objective and Key Result (OKR) is an extension of that which was first invented by google back in 1975, which adds and Objective to which the different KPIs are related to. For instance an objective would be
- Aquire new customers through social media
And the KPIs i.e Key Results, coupled with it would be
Average Post CTR on Facebook
Average Post CTR on Twitter
Average Post CTR on Instagram
Average conversion rate from Facebook visitors
Average conversion rate from Twitter visitors
Average conversion rate from Instagram visitors
etc.
Bounce Rate: The percentage of people who arrive on your website or landing page and leave without viewing any additional pages. On a campaign-specific landing page, your bounce rate is inversely proportional to your conversion rate.
Open Rate: The percentage of people who open your marketing email. Open rate is calculated by dividing the number of emails opened by the total number of emails sent, excluding bounced messages. Many email service providers let you A/B test variables such as subject line and delivery time to help improve your open rate.
CTR: The Click Through Rate (CTR) indicates at how many people see your ad or email versus how many people click on it. You want your click-through rate to be high but optimizing your CTR is only a means to achieving your campaign goal.
Conversion Rate: The percentage of people who complete your campaign goal such as purchase, registration, inquiry or other. If your conversion rate is low, it’s time to optimize your landing page or website.
SEO : Search engine optimization refers to the work to elevate your website on search results.
Backlink: A Link to our website from an outside website
ASO: App Store Optimization, similar to SEO.
SMM: Social Media Marketing, refers to organic (unpaid) marketing on social media. SMO or Social Media Optimization is often used in conjunction with SMM.
PPC : Literally translates to Pay-per-click, but refers to all Media Buying efforts including ad placements on social media, search engines, mobile apps, etc.
SEM : Literally translates to Search Engine Marketing, refers to ad placement purchases on search engines.
CPM: Cost per Impression (CPM) is an ad payment model where you pay for every 1000 impressions i.e views of your ad. This is in contrast to the various types of pay-for-performance advertising, whereby payment is only triggered by a mutually agreed upon activity (i.e. click-through, lead, sale).
CPC: Cost per Click (CPC) is an ad payment model where you pay for each click on your ad instead of just the ad being viewed. If the ad is presented to a user and isn’t clicked, you don’t pay.
CPL: Cost per Lead (CPL) is an ad payment model where you pay for each qualified lead, meaning not only was the ad presented to the user, and not only did he click it, he also filled out a form or clicked a CTA which qualifies him as a lead.
CPA: Cost per Action (CPA) refers to the total cost of converting someone wherein action generally refers to a financial transaction or a purchase engaged by the user. Cost Per Acquisition is the ultimate metric for any marketing department because you don’t want to spend more money to convert a customer than they’re worth.
CPI: Cost per Install (CPI) is an ad payment model where you pay for each app install.
Referral Rate: Your referral rate is the volume of referred purchases as a % of your total purchases. So a 1% referral rate means that 1 in 100 purchases at your store happen through your referral program. An Advocate shares a referral link (typically via social media, email or IM).
Growth: Our growth indicates how our KPI is measuring up in relation to past results per the same KPI.
Specific growth and Average (mean) growth may be calculated via these two simple formulas
$specificGrowth = \frac{present - past}{past}$ Calculates growth between two timestamps
$avgGrowth = (\frac{recentTime}{firstTime})^\frac{1}{n} -1 $ Calculates average growth between n timestamps
Rate: The rate of any KPI such as Churn Rate, Growth Rate, Conversion Rate etc. how our KPIs performance is measuring up in relation to the overall audience it was exposed to.
If for instance we got an average of 20 post likes per day, a month ago, where our entire page followers were 200, and today we have an average of 40 post likes per day with a following of 1200 users, it’s safe to say our user engagement is on the decline.
Rate is simply calculated as such: $\frac{metric}{audience}$
Avearge: While working in digital marketing it’s important to differentiate and understand the different kind’s of averages: Mean, Median, Mode, and Range
Mean: The mean average is what your used to– taking the overall sum and dividing by the number of numbers included.
$$ MeanAvg = \frac{Sum}{#ofNumbers} $$
$ MeanAvg(4,4,4,10,15,15,112) = \frac{164}{7} = 23.43 $
Median: The median average is the middle value in the list of numbers, so if we have 7 numbers such as in (4,4,4,10,15,15,112), the median will be the 4th number (10).
Mode: The mode average is the number appearing the most times. in (4,4,4,10,15,15,112) the number 15 appears twice, and the number 4 appears three times. Therefore the mode of (4,4,4,10,15,15,112) is 4.
Actionable Insight: An insight derived from company data, campaign performance, product performance or other which directs to actions which we should start doing from now on.